Performance Meter
0%
QUESTION ID:1
During translation in prokaryotes, when ribosomes reach the termination codon, the termination codon is recognized by the class I release factors (RF1 or RF2) leading to the release of the polypeptide. A second class II release factor (RF3) facilitates the termination process. Which of the following statements regarding the mechanism of action of the release factors is INCORRECT?
QUESTION ID:2
E. coli DNA ligase catalyses formation of a phosphodiester pond between the adjoining 3' hydroxyl, and the 5' phosphoryl ends in DNA duplexes. The energetic need for this reaction is met by the hydrolysis of NAD+ to NMN+ and AMP in a three-step reaction. Following statements are being made about the mechanism of this reaction.
(i) AMP is linked to the 5' phosphoryl end of the nicked DNA.
(ii) Adenylyl group of NAD+ is transferred to the -amino group of Lys in DNA ligase to form a phosphoamide adduct.
(iii) DNA ligase catalyses the formation of a phosphodiester
bond by the nucleophilic attack of the 3' hydroxyl group onto the phosphate and
releases AMP
Based on the statements made above, identify the correct sequence of the reaction steps.
QUESTION ID:3
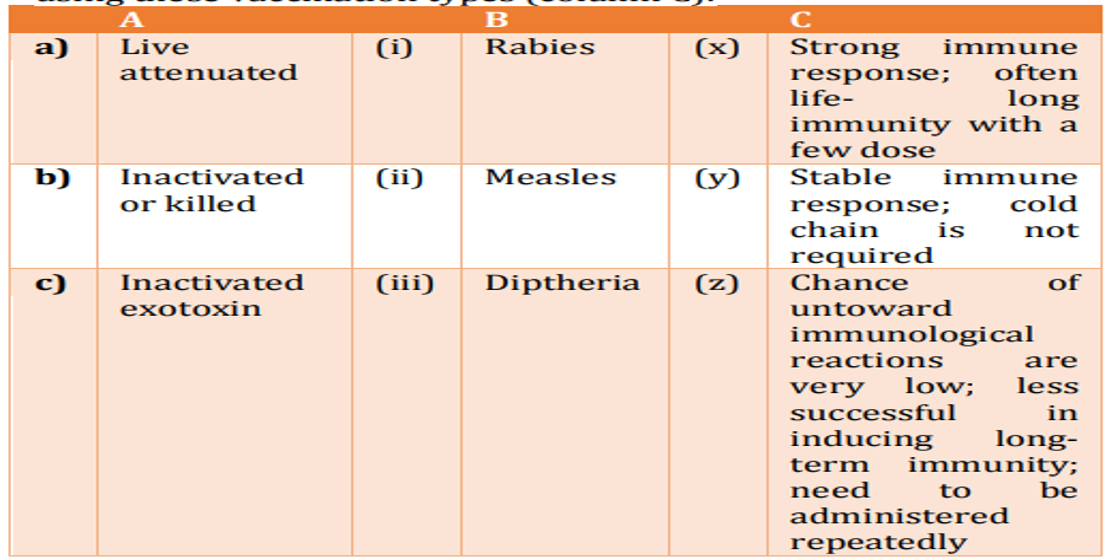
Given below are the types of vaccination (column A), the diseases or conditions against which these vaccination types are used (column 8) and the advantages or disadvantages for using these vaccination types (column C). Which one of the following combinations is the most appropriate match?
QUESTION ID:4
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are used to detect and respond to many different types of signals, including neurotransmitters, hormones involved in glycogen and fat metabolism and even photons of light. Which one of the following statements regarding GPCR is INCORRECT?
QUESTION ID:5
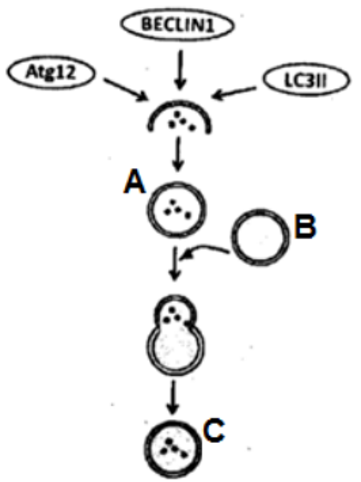
The following intracellular event occurs in a cell that is subjected to conditions of starvation. Which one of the following statements correctly represents the event shown above?
QUESTION ID:6
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex combination of secreted proteins that is involved in holding cells and tissues together. The components of ECM form a network by binding to each other and communicate with cells by binding to adhesion receptors on the cell surface. ECM comprises mainly two classes of macromolecules, proteoglycans and very high molecular weight large proteins.
Which one of the following statements regarding ECM constituents is INCORRECT?
QUESTION ID:7
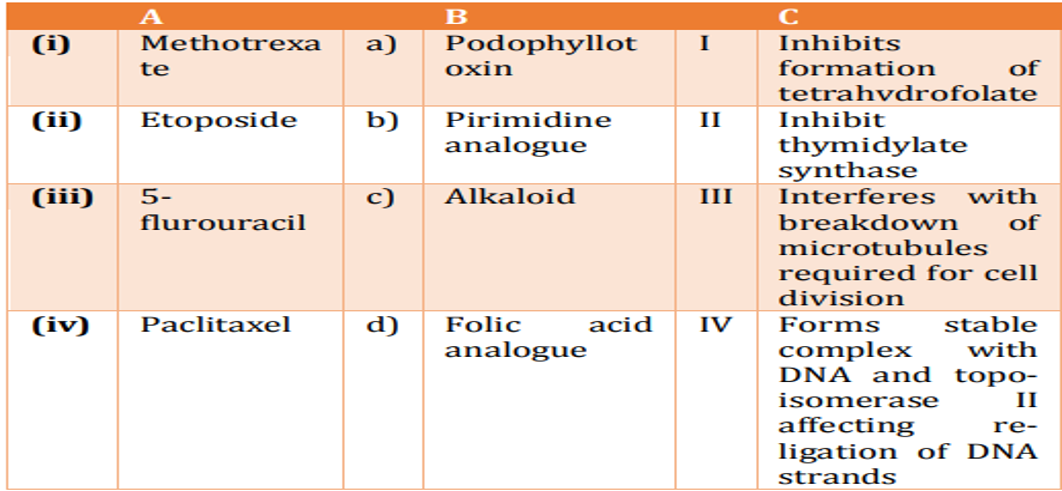
Present-day cancer treatment uses many approaches. Beyond surgery and radiation treatment, which are most often employed in cases of larger, more discrete tumors, drug therapies can be used to target residual tumor cells and to attack dispersed cancers. Chemotherapies by anti-cancer drugs are mostly aimed at blocking DNA synthesis and cell division. A list of anti-cancer drugs is given in column A, their chemical nature in column Band their mechanism of action in column C.
QUESTION ID:8
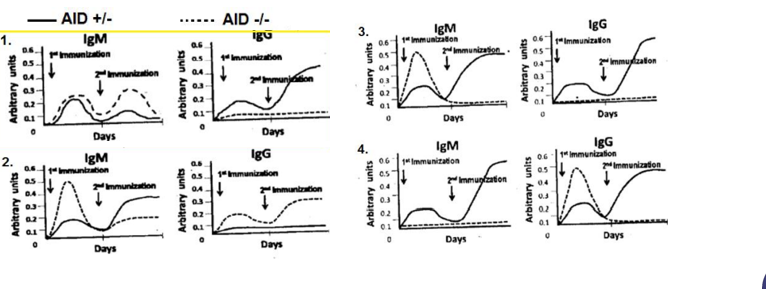
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is the key mediator of somatic hypermutation, gene conversion and classswitch recombination. In order to ascertain the role of AID in class-switch recombination, immune response against a target antigen was compared between AID knock-out mice (AID-/-) with that of mice retaining a functional copy of the AID gene (AID+/-). Development of IgM and IgG antibodies against the target antigen was then measured following successive immunization and plotted graphically. Which one of the following is the most appropriate representation of the experiment?
QUESTION ID:9
Following statements were made regarding vulval development in Caenorhabditis elegans:
A. The six vulval precursor cells (VPCs) are influenced by the anchor cell to form an equivalence group.
B. In the loss of function lin-12 mutants, both cells become uterine whereas in gain of function mutants, both become anchor cell.
C. If the anchor cell is destroyed early in development, all the six VPCs divide once and contribute towards the formation of hypodermal cells.
D. The anchor cell/ventral uterine precursor decision is due to Notch-Delta mediated mechanism of restricting adjacent cell fates.
E. The paracrine factor secreted by the anchor cell directly activates the Notch-delta pathway.
Which one of the following options represents a combination of correct statements?
QUESTION ID:10
Given below are few statements regarding the role of Disheveled (Dsh) and β-catenin (β-cat) in the development of sea urchin.
A. Dsh is localized in the vegetal cortex of the oocyte before fertilization and in the region of the 16-cell embryo about to become the micromeres.
B. Dsh is localized in the cytosol of the oocyte during oogenesis and in the micromere forming blastomeres of a 16- cell embryo.
C. β-cat accumulates predominantly in the micromeres and somewhat in the veg2 tier cells.
D. Treatment of embryos with lithium chloride does not allow the accumulation of β-cat in the nuclei of all blastula cells, and the animal cells thus become specified as endoderm and mesoderm
E. When β-cat is prevented from entering the nucleus, the embryo develops as a ciliated ectodermal ball.
Which one of the following options represents a combination of correct statements?
QUESTION ID:11
Which one of the following statements regarding limb regeneration in Salamander is correct?
QUESTION ID:12
QUESTION ID:13
cAMP signalling plays a very important role in the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Below are few statements related to it.
A. Every amoeba at the time of aggregation has the potential to make, receive and relay cAMP.
B. acb- mutants develop normally but the spores formed appear glassy and are unable to germinate.
C. The spores formed by the acg- mutants germinate in the sorus itself.
D. RegA is an extracellular phosphodiesterase.
E. cAMP is continuously secreted in nanomolar amounts during aggregation.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
QUESTION ID:14
Torpedo, is known to serve as a receptor for Gurken. Deficiencies of the torpedo gene in Drosophila cause ventralization of the embryo. In an experiment, the germ cell precursors from a wild type embryo were transplanted into embryos whose mother carried the torpedo mutation. Also, the reverse experiment, i.e., transplantation of germ cell precursors from torpedo mutants into wild type embryos was done. The torpedo deficient germ cells developed in a wild type female showed normal dorso-ventral axis, while the wild type germ cells developed in a torpedo deficient female showed ventralized egg.
Some of the following statements are drawn from the above experiments and some from known facts to understand the functioning of Torpedo.
A. Zygotic contribution of Torpedo is essential for the development of dorso- ventral axis.
B. Maternal contribution of Torpedo is essential for the development of dorso- ventral axis.
C. Since Torpedo is a receptor for Gurken and follicle cells surround the part of the oocyte where Gurken is expressed, it is likely that Torpedo is expressed in follicle cells. ·
D. Gurken signalling initially dorsalizes the follicle cells, which in turn send signal to organize the dorso-ventral polarity in oocyte.
E. Gurken signalling initially dorsalizes the nurse cells which help in generation of dorso-ventral polarity in oocyte.
Which one of the following combination of statements is most appropriate?
QUESTION ID:15
Stomata from detached epidermis of common dayflower (Commelina communis) were treated with saturating photon fluxes of red light. In a parallel treatment, stomata treated withred light were also illuminated with blue light (indicated by arrow). From the graphs shown below, select the correct pattern of stomata opening (solid lines and dotted lines represent stomatal aperture under red and blue lights, respectively).
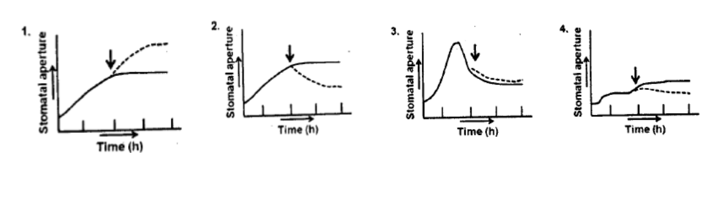
QUESTION ID:16
Following are certain statements regarding Rubisco, the predominant protein in plant leaves that catalyzes the initial reaction of the Calvin-Benson cycle.
A. During the oxygenase activity of Rubisco, O2 is used as substrate to produce three carbon molecule, 3- phosphoglyceratc and two-carbon molecule, 2 phosphoglycolate.
B. In red and brown algae, the large subunit of Rubisco is localized in the chloroplast while small subunit is localized in the nucleus.
C. The bound sugar phosphates in Rubisco are specifically removed by an ATP dependent enzyme, Rubisco activase.
D. Catalytic activities of rubisco—require the formation of a lysyl-carbamate by a molecule of CO2 called activator CO2.
Which one of the following combinations of above statements is correct?
QUESTION ID:17
Given below are certain statements regarding plantpathogen Interactions:
A. The pattern recognition receptor (PRR), upon perceiving pathogen or microbe associated patterns (PAPMs/MAMPs), activates plant defenses resulting in pattern triggered immunity (PTI).
B. AvrPto is a resistance gene in tomato that acts against pathogenic attack by the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato.
C. The effector molecules produced by pathogen is recognized by resistance (R) gene present in plants resulting into a defense strategy known as effector triggered immunity (ETI).
D. Defense mechanisms triggered in plants during PTI are usually stronger than those during ETI.
Which one of the following combinations of above statements is correct?
QUESTION ID:18
To characterize the mechanism/s by which heat-stress is perceived in Arabidopsis, a team of researchers fused a Heat Shock promoter with luciferase gene. Transgenic plants having promoter: luciferase fusion were raised. Such plants revealed strong luciferase expression upon heat-stress but they showed no expression under unstressed control condition. Subsequently, these transgenic plants were mutagenized by EMS and seeds from F2 generation were obtained. To analyze the downstream positive regulators of heat-stress, the researchers should analyze seedlings that are
QUESTION ID:19
Two near inbred parental lines P1 and P2 of an angiosperm species are crossed to produce F1 seeds in which, the ploidy of the endosperm is 6N. If plants generated from these F1 seeds are backcrossed with P1, what will be the ploidy of the somatic cells in the next generation?
QUESTION ID:20
The table given below represents the types of intercellular transport in "Column I" in land plants and their transport pathways in “Column II” Which one of the following combinations matches column I correctly with column II
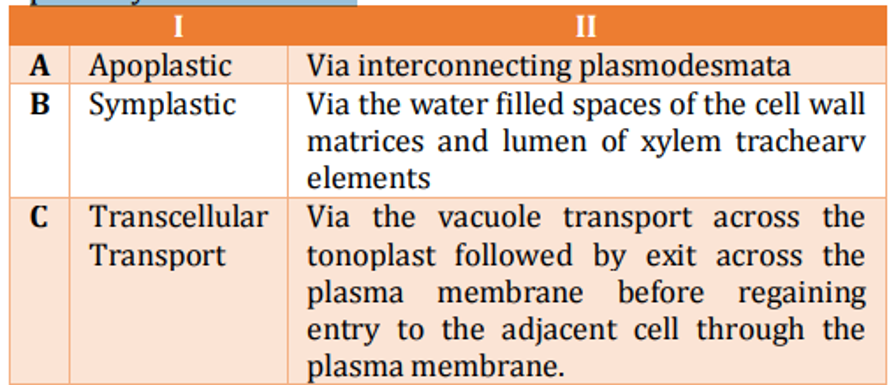
QUESTION ID:21
The Cl content of red blood cells (RBCs) in the venous blood was found to be higher than that in arterial blood in a human subject. Following proposals were made to explain these observations:
A. The high pCO2 in venous plasma leads to increased diffusion of CO2 into RBC and the formation of H2CO3.
B. HCO3 - content in the RBC of venous blood becomes much greater than that in plasma.
C. The excess HCO3 - leaves the RBC of venous blood along with Na+ to plasma by a Na+ - HCO3 -symporter,
D. The increased Na+ in the venous plasma is transported to the RBC along with Cl .
Select the combination with INCORRECT statements from the following options.
QUESTION ID:22
The different waves of normal electrocardiogram (ECG) of a human subject are shown below
The relationship of the events of cardiac cycle to these ECG waves are proposed in the following statements:
A. The P wave occurs due to the depolarization of atria
B. The atrial repolarization is responsible for the T wave
C. The QRS complex occurs during ventricular depolarization
D. Q - T interval indicates plateau portion of auricular action potential
Select the combination with INCORRECT statements from the following options:
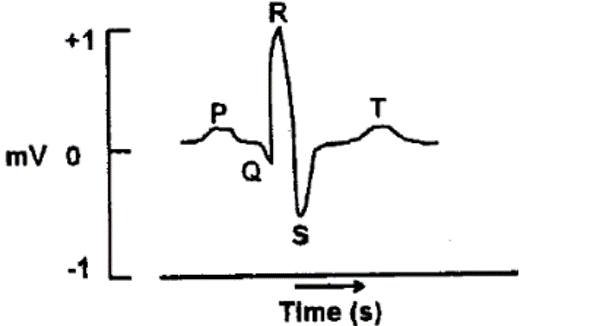
QUESTION ID:23
The excitation of auditory hair cells by the displacement of stereocilia has been explained in the following proposed statements:
QUESTION ID:24
The peaks of the compound action potential (i.e., A, B and C) recorded from a mammalian mixed nerve were affected after application of increasing pressure on the nerve. Some probable changes of compound action are stated below:
A. 'A' peak was inhibited by lower intensity of pressure
B. 'C' peak was inhibited by higher intensity of pressure
C. 'B' peak was inhibited by lower intensity of pressure
D. 'C' peak was inhibited by lower intensity of pressure
E. 'A' peak was inhibited by higher intensity of pressure
Select the option with the combination of CORRECT statements.
QUESTION ID:25
The different segments of renal tubule (column A) and the mechanism of Na+ transport in the apical membrane of tubular cells (column B) are tabulated below: Select the option with the correct matches:
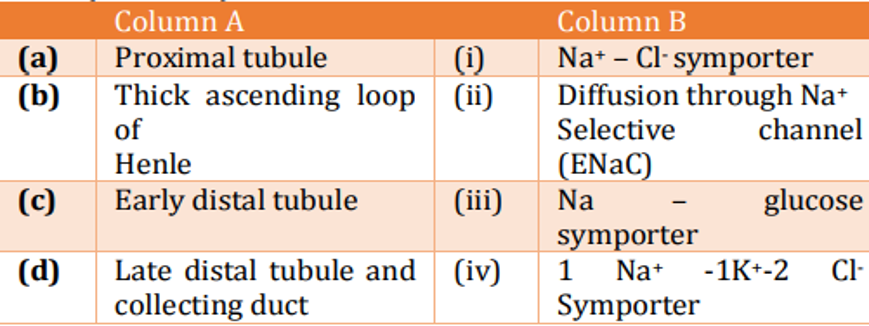
QUESTION ID:26
The figure below represents normal sex determination, differentiation and development in humans Identify A, B, C and D.
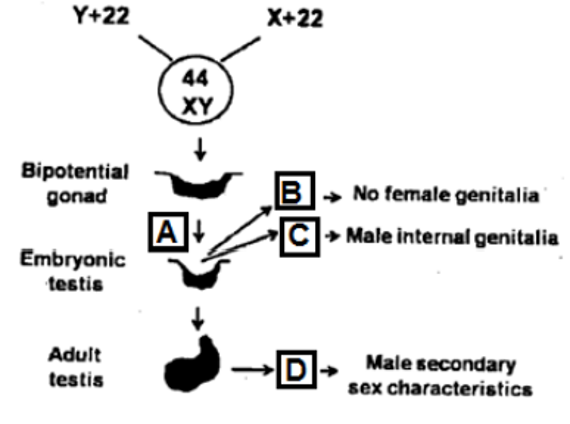
QUESTION ID:27
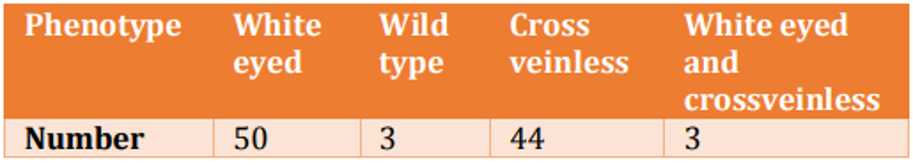
A virgin Drosophila female was crossed with a wild type male. The F1 progeny obtained had four types of males as shown below
Assuming that white eye and crossveinless mutations are Xlinked and recessive, the following statements were made:
A. F1 females were also of four types as that of males.
B. The white eyed crossveinless male flies appeared due to independent assortment.
C. The map distance between the genes for white eye and crossveinless is estimated to be 12 cM.
D. The map distance between white eye and crossveinless is estimated to be 6 cM.
E. All F1 females are expected to be wild type.
F. The F1 wild type males appeared due to crossing over.
The combination with correct statements is:
QUESTION ID:28
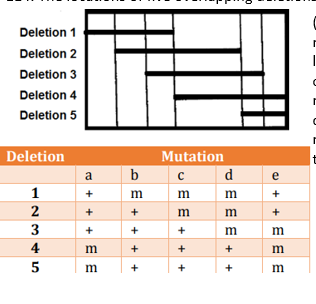
The locations of five overlapping deletions have been mapped to a Drosophila chromosome as shown below (Horizontal lines in the above figure indicate the deleted regions) Recessive mutations a, b, c, d and e are known to be located within this region, but the order of mutations on the chromosome is not known. When the flies homozygous for the recessive mutations are crossed with flies homozygous for the deletions, the following results are obtained (letter "m" represents mutant phenotype and "+'' represents the wild type)
On the basis of the above data, the relative order of the five mutant genes on the chromosome is
QUESTION ID:29
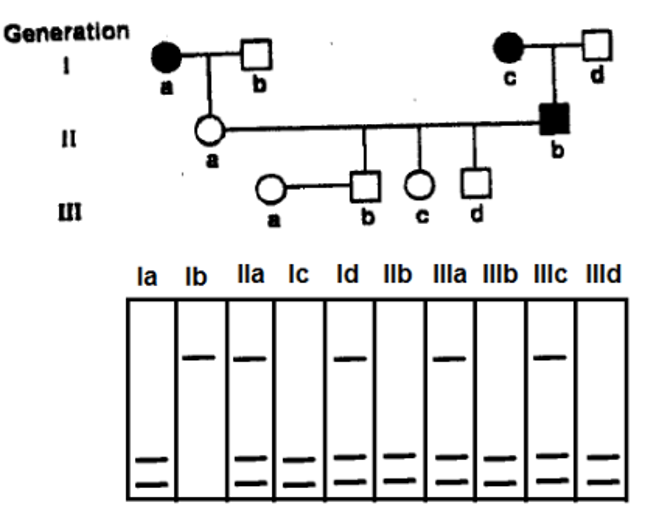
The pedigree given below follows the inheritance pattern of a late-onset (after age of 30 years) genetic disease that is 100% penetrant. Affected individuals are indicated by a solid circle (woman) or solid ·square (males). RFLP analysis of DNA from each individual is shown below in the pedigree.
Which grandchildren (IIIb to IIId) will be affected by the disease after attaining the age of 30 years?
QUESTION ID:30
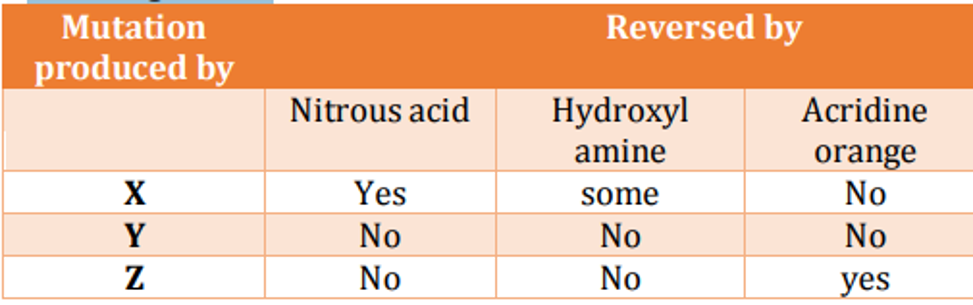
A chemist synthesizes three new chemical compounds in the laboratory and names them as X, Y and Z. After analysing mutagenic potential of all these compounds, the geneticist observed that all are highly mutagenic. The geneticist also tested the potential of mutations induced by these compounds to be reversed by other known mutagens and obtained the following results
Assuming that X, Y and Z caused any of the three types of mutations, transition, transversion or single base deletion, what conclusions can you make about the nature of mutations produced by these compounds?
QUESTION ID:31
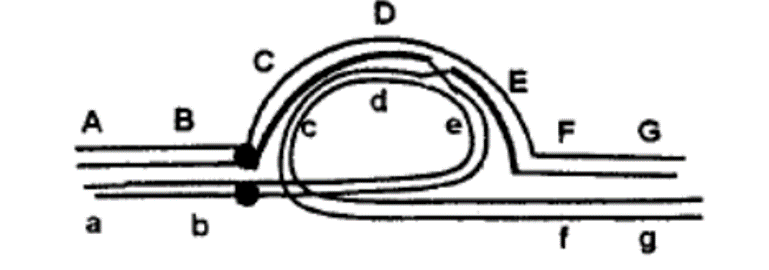
An individual is having an inversion in heterozygous condition. The regions on normal chromosome are marked as A, B, C, D, E, F, G while the chromosome having inversion has the regions as a, b, e, d, c, f, g. The diagram given below shows pairing of these two homologous chromosomes during meiosis and the site of a crossing over is indicated:
The following statements are given to describe the inversion and the consequence of crossing over shown in the above diagram:
A. This is a pericentric inversion
B. This will generate a dicentric and an acentric chromosome following separation of chromosomes after crossing over
C. This will generate two monocentric recombinant chromosomes following separation of chromosomes after crossing over
D. All the gametes thus formed will have deletion and/or duplication and will be non-viable
E. 50% of the gametes having recombinant chromatid will be non-viable, while 50% gametes having non-recombinant chromatid will survive
F. This is a paracentric inversion
Which combination of the above statements describe the inversion and meiotic consequences correctly
QUESTION ID:32
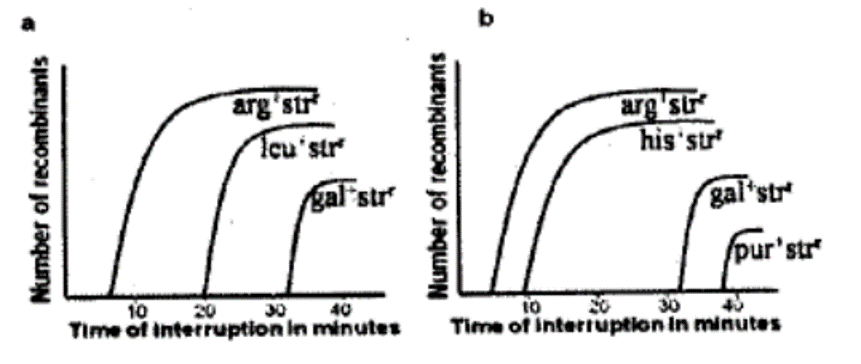
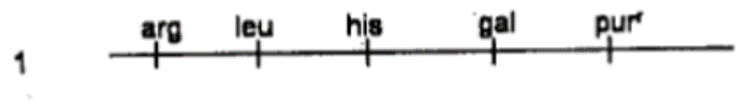
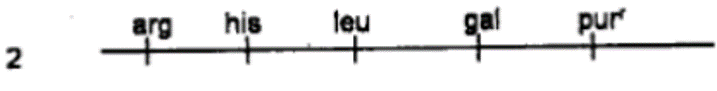
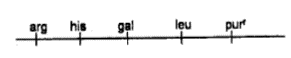
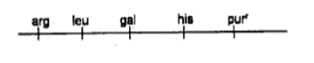
QUESTION ID:33
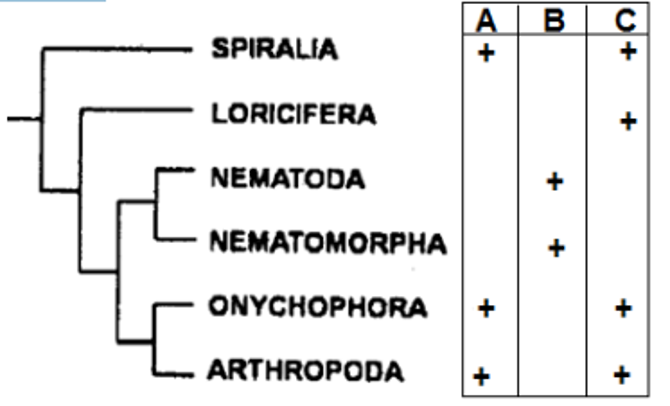
Three anatomical characteristics (A, B and C) of invertebrate nervous system are used to build a generalized cladogram given below. Presence of the anatomical character is indicated by '+'
Based on the pattern of character distribution, pick the correct combination that are represented by A, B and C
QUESTION ID:34
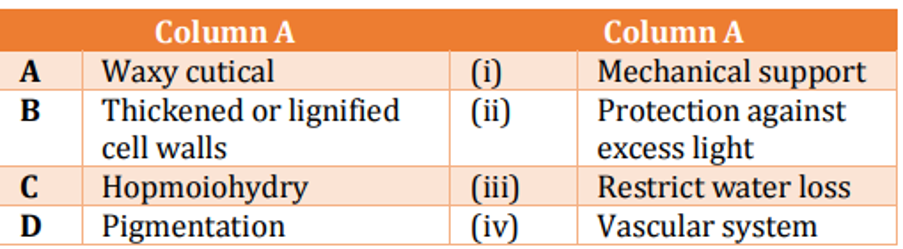
In order to survive in a non-aquatic environment, plants acquired several adaptations with specialized functions. Given below is a list of features/characteristics (Column A) and their potential role (Column B).
Which one of the following options represents a correct match between the adaptations and their functions?
QUESTION ID:35
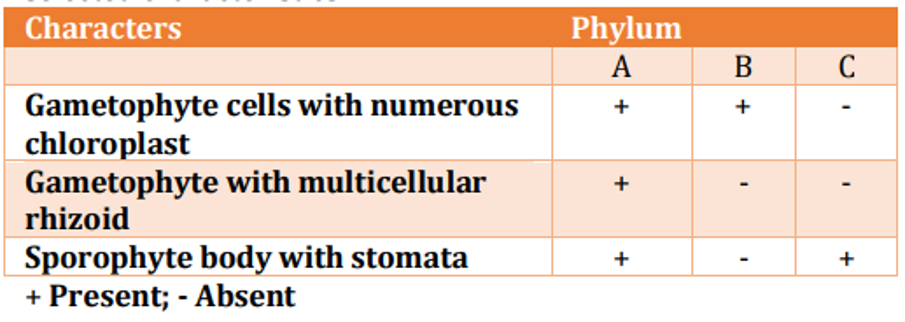
Following table presents bryophyte phyla with their selected characteristics: In the above table, phyla A, B and C represent
QUESTION ID:36
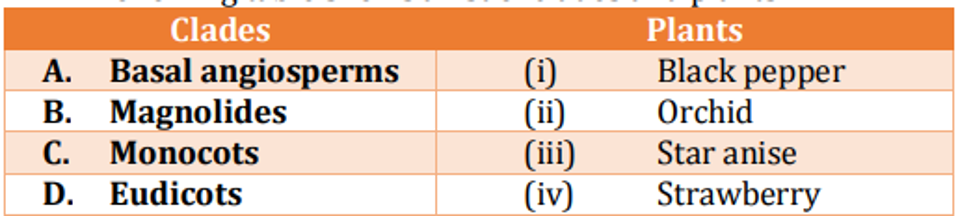
Following table shows a list of clades and plants: Which one of the following is a correct match for the above?
QUESTION ID:37
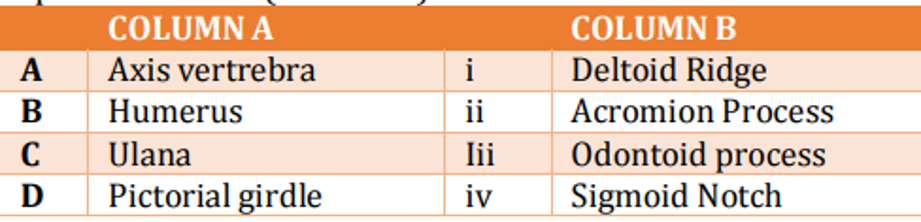
The following table shows names of bones (Column A) and specific features (Column B). Which one of the following options gives the correct match of the bones with their specific features?
QUESTION ID:38
The figure below shows the nervous system of Mollusca with ganglia and the connecting nerves. The connecting nerves are labelled as A, B, C and D. Which one of the following options has correct labelling of A, B, C and D?
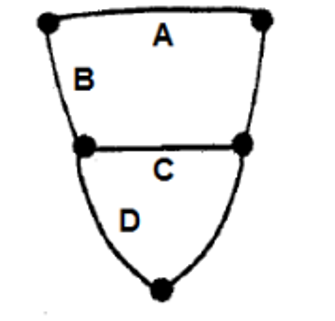
QUESTION ID:39
Following are certain statements regarding energy efficiencies of ectotherms and endotherms:
A. Ectotherms have high assimilation efficiency but low production efficiency.
B. Ectotherms have low assimilation efficiency but high production efficiency.
C. Endotherms have high assimilation efficiency but low production efficiency.
D. Endotherms have low assimilation efficiency but high production efficiency.
Which one of the following represents the combination of correct statements?
QUESTION ID:40
Given below are some properties related to botanical and zoological nomenclature.
A. Absence of tautonyms
B. Presence of genus and species ranks only
C. Absence of principle of coordination
D. Presence of only holotype and neotype
Select the correct combination that distinguishes botanical nomenclature from zoological nomenclature system.
QUESTION ID:41
Following table gives a list of international environmental agreements and areas covered. Which of the following is correct combination?
QUESTION ID:42
The following figure is a "risk-graph" that illustrates the percent risk a species faces towards extinction The following are ranks assigned according to IUCN's red-list category:
(i) Critically endangered
(ii) Near threatened
(iii) Vulnerable
(iv) Least concern
Which one of the following is the most appropriate match between the percent-risk and their assigned rank?
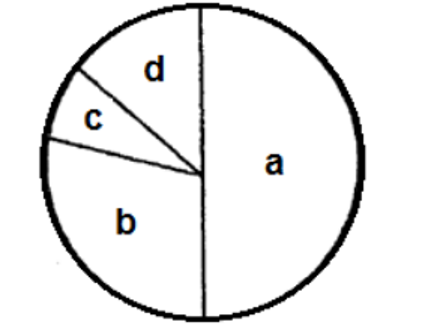
QUESTION ID:43
The complexity of a food web in a community is quantified using certain parameters which are defined below. Which of the following is an INCORRECT representation?
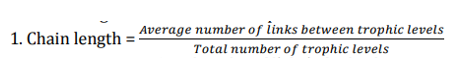
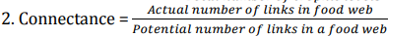

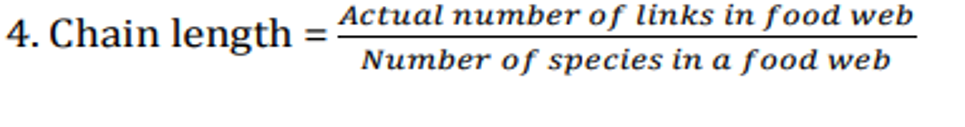
QUESTION ID:44
The above graph illustrates two lines that represent the immigration and extinction rates for an island based on its distance from mainland (solid line) and its size (dotted line). Which of the following is true for this island?
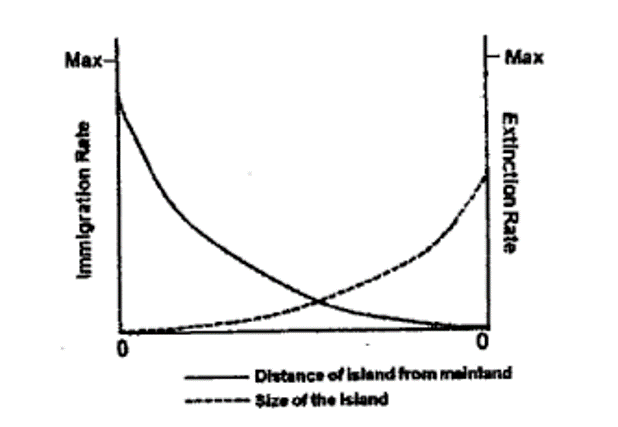
QUESTION ID:45
Inclusive fitness of an animal can be measured as a sum of direct fitness and indirect fitness. Imagine you have 10 off springs. Through diligent parental care, 5 survive to reproduce. You give your life in a heroic deed to save a total of 5 of your nieces and nephews. What is your inclusive fitness?
QUESTION ID:46
Altruism describes a behaviour performed by animals that may be disadvantageous to self while benefitting others. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT about altruism?
QUESTION ID:47
Given are some statements with reference to the use of genes in plant molecular systematics.
A. mtDNA are not preferred over cpDNA or rDNA because they generally show slow rate of sequence evolution and fast rate of structural evolution.
B. cpDNA are not preferred because of their haploidy, uniparental inheritance, and absence of recombination among cpDNA molecules.
C. rDNA such as ITS are preferred for their higher evolutionary rates as well as shorter sequence length.
D. rDNA and cpDNA cannot be used simultaneously in molecular systematics since they represent conflicting patterns of inheritance.
Which of the above statements are INCORRECT?
QUESTION ID:48
Following are key points about the effect of genetic drift:
A. Genetic drift is significant in small populations.
B. Genetic drift can cause allele frequencies to change in a predirected way.
C. Genetic drift can lead to a loss of genetic variation within populations.
D. Genetic drift can cause harmful alleles to become fixed.
Which one of the following combination of the above statements are true?
QUESTION ID:49
Following table contains some of the generalizations of evolutionary biology: Which of the following is correct match between Column I and II?
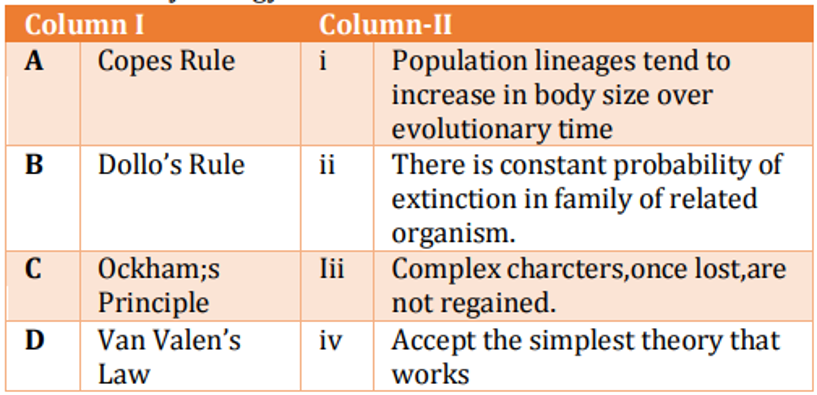
QUESTION ID:50
A 1257 bp genomic DNA sequence of a prokaryotic gene was cloned under a strong constitutive promoter along with a suitable polyA signal and used for development of transgenic tobacco plants. Molecular analysis revealed the presence of three types/lengths of transgene derived mRNAs: 555 bp, 981 bp and 1257 bp - in the leaves of transgenic plants. The following statements were proposed to explain the above results.
A. The three mRNAs represent alternatively spliced transcripts due to the presence of putative intronic sequence in the gene.
B. The gene sequence was characterized by the presence of potential polyadenylation signals that resulted in premature termination of transcription.
C. Expression of full-length transcripts (1257 bases) was lethal to the transformed cells.
D. The transgenic plants were chimeric in nature and comprised of a mix of transformed and untransformed cells.
Which of the following combinations of the above statements would correctly explain the obtained results?
QUESTION ID:51
In order to detect minor variations in antigen concentration, the following procedures were suggested. Which one will likely be the best option?
QUESTION ID:52
Three students (P, Q, R) in a research lab were trying to identify proteins that interact with a transcription factor X. P performed gel filtration experiments and identified that X was found along with proteins A, B, C and D. Q performed coimmunoprecipitation experiments using antibodies to X and identified A, B and C. R did a yeast-2-hybrid screen and identified only B.
The following are likely conclusions that may explain all the results:
(i) A, B, C and D are in a complex with X.
(ii) X directly interacts with B.
(iii) Only A, Band C are in complex with X.
(iv) D is probably weakly associated with X.
Which of the above conclusions best explains all the results?
QUESTION ID:53
Sub-cellular fractionation-based assays have been used to identify various organelles in the mammalian cells. In order to characterize such organelles in a living mammalian cell, which of the following microscopy-based method would be the most accurate?
QUESTION ID:54
From the following statements,
A. Surface plasmon resonance can be used to determine binding constants only in the range of 102 - 103 M.
B. de novo sequencing is not possible by mass spectral methods.
C. The position of hydrogen atoms in proteins is not directly determined by X-ray, diffraction.
D. Circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy do not give the same information on protein structure.
Choose the option with all correct statements.
QUESTION ID:55
A researcher attempted to clone two genes (X and Y) independently in a plasmid vector for over expression and purification in E. coli. All attempts to clone gene X were unsuccessful whereas gene 'Y' could be cloned easily. When the, researcher attempted to clone gene 'X' in the plasmid clone containing gene 'Y', gene 'X' could be cloned. The following statements were proposed to explain the above results.
A. Protein encoded by gene 'Y' is not lethal to the cell.
B. Gene 'X' has introns, which prevents its expression in E. coli
C. Expression of 'X' protein is lethal to the cell.
D. The 'Y' gene product inhibits the activity of 'X' protein
Which one of the following options represents a combination of correct statements to explain the observations?
QUESTION ID:56
In order to visualize the intracellular organization of a cell, one can utilize various microscopy-based techniques. These include:
A. Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy
B. Phase contrast microscopy
C. Dark field microscopy
D. Epifluorescence microscopy
E. Scanning electron microscopy
F. Transmission electron microscopy
G. Confocal microscopy
Which of the above mentioned microscopes can be used to study the intracellular dynamics using live cell imaging?
QUESTION ID:57
A certain protein has been assumed to play an indispensable role in the survival of an intracellular parasite inside the host cells. Which one of the following techniques will best prove the assumption to be correct?
QUESTION ID:58
Given below is a table with information on isotopes, their half-life and type of particle(s) they emit. Choose the correct combination from the options given below.
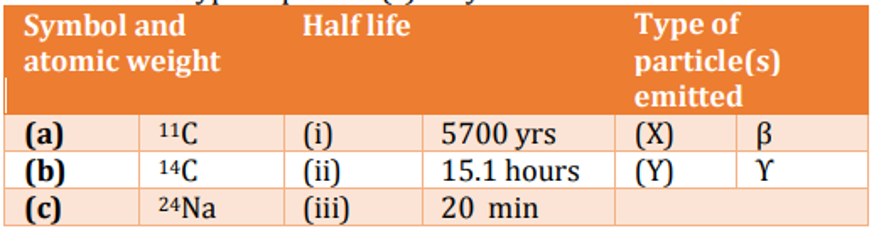
QUESTION ID:59
Which one of the following set of essential components are required for Sanger method of DNA sequencing in a required buffer containing MgCl2 and Tris-HCl?
 TLS Online
TLS Online