Performance Meter
0%
QUESTION ID:1
QUESTION ID:2
QUESTION ID:3
QUESTION ID:4
QUESTION ID:5
QUESTION ID:6
QUESTION ID:7
QUESTION ID:8
The data given in the following table summarizes the monthly budget of an average household
The approximate percentage of the monthly budget NOT spent on savings is
QUESTION ID:9
QUESTION ID:10
QUESTION ID:11
Among the following, the most reactive diene in the Diels-Alder reaction is
QUESTION ID:12
QUESTION ID:13
QUESTION ID:14
QUESTION ID:15
The non-aromatic compound/ion is
QUESTION ID:16
QUESTION ID:17
QUESTION ID:18
QUESTION ID:19
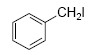
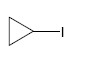
QUESTION ID:20
QUESTION ID:21
QUESTION ID:22
QUESTION ID:23
[FeCl4]2– (I), [CoCl4]2– (II) and [NiCl4]2– (III) are paramagnetic tetrahedral complexes.
The order of values of spin only magnetic moment is
QUESTION ID:24
QUESTION ID:25
The structure of the product obtained is
QUESTION ID:26
QUESTION ID:27
QUESTION ID:28
QUESTION ID:29
QUESTION ID:30
QUESTION ID:31
QUESTION ID:32
Match the hormones in Group I with their metabolic precursor in Group II
| Group I | Group II |
| P. 17-β estradiol | 1. Arachidonic acid |
| Q. Thromboxane A2 | 2. Tyrosine |
| R. Epinephrine | 3. β-carotene |
| S. Retinoic acid | 4. Cholesterol |
QUESTION ID:33
QUESTION ID:34
QUESTION ID:35
QUESTION ID:36
QUESTION ID:37
QUESTION ID:38
QUESTION ID:39
QUESTION ID:40
QUESTION ID:41
QUESTION ID:42
Match the enzymes in Group I with their corresponding activity in Group II
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Flippase | 1. Catalyzes the movement of any phospholipid across the lipid bilayer down its concentration gradient |
| Q. Floppase | 2. Catalyzes the translocation of amino-phospholipids from the extrace |
| R. L | 3. Catalyzes the translocation |
| S. Scramblase | 4. Degradation of phospholipids from the lipid bilayer including the inner and outer l |
QUESTION ID:43
Match the antibiotics in Group I with their mechanism of action in Group II
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Tetracyclines | 1. Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by blocking peptidyl transfer |
| Q. Chloramphenicol | 2. Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by blocking the A-site on the ribosome |
| R. Cycloheximide | 3. Misreads the genetic code |
| S. Streptom | 4. Inhibits protein synthesis by blocking peptidyl transferase on 80S ribo |
QUESTION ID:44
QUESTION ID:45
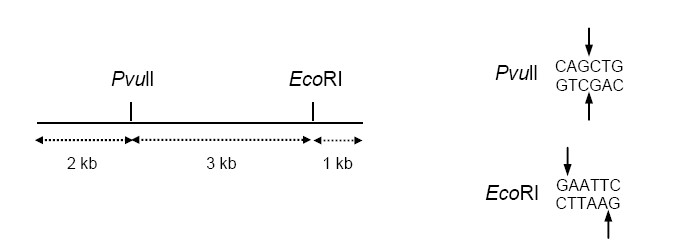
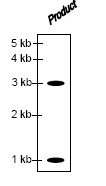
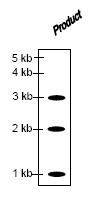
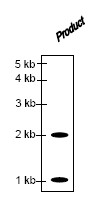
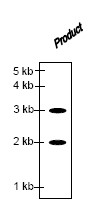
QUESTION ID:46
QUESTION ID:47
QUESTION ID:48
QUESTION ID:49
QUESTION ID:50
QUESTION ID:51
QUESTION ID:52
QUESTION ID:53
QUESTION ID:54
QUESTION ID:55
QUESTION ID:56
QUESTION ID:57
QUESTION ID:58
| Recombinant proteins | Applications |
| P. Hirudine | 1. HIV therapy |
| Q. Trichosanthin | 2. Anticoagulant |
| R. Somatotrophin | 3. Growth hormone |
| S. β-Interferon | 4. Hypertension |
| 5. Cystic fibrosis | |
| 6. Treatment for hepatitis-B |
QUESTION ID:59
QUESTION ID:60
QUESTION ID:61
QUESTION ID:62
QUESTION ID:63
QUESTION ID:64
QUESTION ID:65
Match the name of the disease with the causal organism
| Disease | Causal organism |
| P. Black rot of sugarcane | 1. Cercospora personata |
| Q. Stem rot of jute | 2. Macrophomina phaseolina |
| R. Tikka disease of groundnut | 3. Ceratocystis adiposa |
| S. Crown gall of grapes | 4. Synchytrium endobioticum |
| 5. Agrobacterium | |
| 6. Colletotrichum corc |
QUESTION ID:66
QUESTION ID:67
QUESTION ID:68
QUESTION ID:69
QUESTION ID:70
QUESTION ID:71
QUESTION ID:72
QUESTION ID:73
QUESTION ID:74
Match the disease in Group I with their corresponding organism in Group II
| Group I | Group II |
| P. African sleeping sickness | I. Rubulavirus |
| Q. Rocky mountain spotted fever | II. Trypanosoma brucei |
| R. Mumps | III. Wuchereria bancrofti |
| S. Filariasis | IV. Rickettsia rickettsii |
| V. Leishmania donovani |
QUESTION ID:75
QUESTION ID:76
QUESTION ID:77
QUESTION ID:78
Match the Phylum in Group I with their characteristic motility appendage listed in Group II
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Archaezoa | I. Flagella |
| Q. Amoebozoa | II. Fimbriae |
| R. Ciliophora | III. Pseudopods |
| S. Apicomplexa | IV. Cilia |
| V. Pili |
QUESTION ID:79
QUESTION ID:80
QUESTION ID:81
QUESTION ID:82
QUESTION ID:83
QUESTION ID:84
QUESTION ID:85
QUESTION ID:86
QUESTION ID:87
QUESTION ID:88
QUESTION ID:89
QUESTION ID:90
QUESTION ID:91
QUESTION ID:92
QUESTION ID:93
QUESTION ID:94
QUESTION ID:95
QUESTION ID:96
QUESTION ID:97
QUESTION ID:98
QUESTION ID:99
QUESTION ID:100
QUESTION ID:101
QUESTION ID:102
QUESTION ID:103
QUESTION ID:104
QUESTION ID:105
QUESTION ID:106
QUESTION ID:107
QUESTION ID:108
QUESTION ID:109
QUESTION ID:110
QUESTION ID:111
QUESTION ID:112
QUESTION ID:113
QUESTION ID:114
QUESTION ID:115
QUESTION ID:116
QUESTION ID:117
QUESTION ID:118
Make the correct match of the food constituents in Group I with their nature given in Group II.
| Group I | Group II |
| P) Ascorbic Acid | 1) Sugar |
| Q) Phenyl alanine | 2) Chelate |
| R) Dextrose | 3) Amino Acid |
| S) Haemoglobin | 4) Antioxidant |
QUESTION ID:119
| Group I | Group II |
| P) Yoghurt | 1) Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii |
| Q) Cheese | 2) Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Lactobacillus plantarum |
| R) Sauerkraut | 3) Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Streptococcus thermophillus |
| S) Kefir | 4) Lactobacillus casei and Streptococcus thermophillus |
QUESTION ID:120
| Group I | Group II |
| P) Cytoplasmic membrane | 1) Protein synthesis |
| Q) Flagellum | 2) Peptidoglycan |
| R) Cell wall | 3) Phospholipid bilayer |
| S) Ribosome | 4) Motility of cell |
QUESTION ID:121
QUESTION ID:122
| Group I | Group II |
| P) Ball Mill | 1) Compression and shear |
| Q) Roller Mill | 2) Pressure bursting |
| R) Flash Peeling | 3) Friction and shear |
| S) Abrasive Peeling | 4) Impact and shear |
QUESTION ID:123
QUESTION ID:124
QUESTION ID:125
 TLS Online
TLS Online