Performance Meter
0%
QUESTION ID:1
QUESTION ID:2
QUESTION ID:3
QUESTION ID:4
QUESTION ID:5
QUESTION ID:6
QUESTION ID:7
QUESTION ID:8
QUESTION ID:9
QUESTION ID:10
QUESTION ID:11
Hybridizations of nitrogen in NO2+, NO3−, NH4+ respectively are
QUESTION ID:12
QUESTION ID:13
QUESTION ID:14
The major product formed in the following reaction is
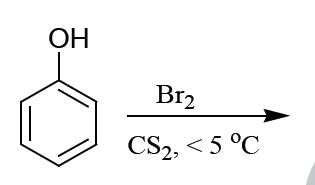
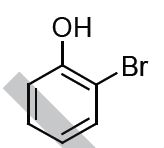
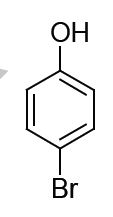
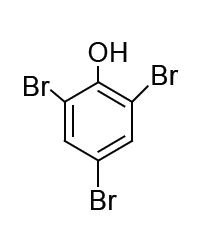
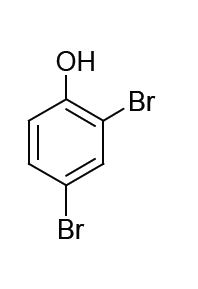
QUESTION ID:15
QUESTION ID:16
QUESTION ID:17
QUESTION ID:18
QUESTION ID:19
QUESTION ID:20
QUESTION ID:21
QUESTION ID:22
QUESTION ID:23
The Fisher projection that represents (2R,3S)-2,3-dihydroxybutanoic acid is
QUESTION ID:24
QUESTION ID:25
The order of acidity of the following acids is
QUESTION ID:26
QUESTION ID:27
QUESTION ID:28
QUESTION ID:29
QUESTION ID:30
QUESTION ID:31
QUESTION ID:32
QUESTION ID:33
QUESTION ID:34
QUESTION ID:35
QUESTION ID:36
QUESTION ID:37
QUESTION ID:38
QUESTION ID:39
| Group I | Group II |
| P) J chain | 1) VDJ recombinase complex |
| Q) Serpin | 2) Component of MHC class I |
R) β2-microglobulin | 3) B cell co-receptor complex |
| S) Artemis | 4) C1 complement inhibitor |
| 5) Component of MHC class II | |
| 6) Mult |
QUESTION ID:40
QUESTION ID:41
QUESTION ID:42
Shown below is an electrospray ionization mass spectrum of a protein:
The numbers written on top of the peaks are the m/z values. The mass of the protein deduced from the given data is ___________ kDa
QUESTION ID:43
QUESTION ID:44
QUESTION ID:45
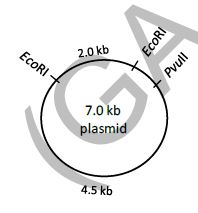
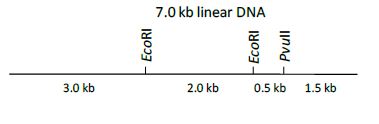
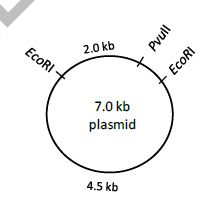
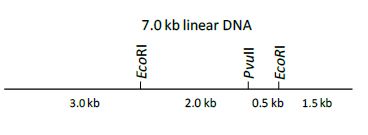
QUESTION ID:46
QUESTION ID:47
QUESTION ID:48
QUESTION ID:49
QUESTION ID:50
QUESTION ID:51
QUESTION ID:52
QUESTION ID:53
| Column I | Column II |
| P. Saffron | 1. Garcinia sp. |
| Q. Gamboge | 2. Rocella tinctoria |
| R. Litmus | 3. Crocus sativus |
| S. Turmeric | 4. Curuma sp. |
QUESTION ID:54
QUESTION ID:55
QUESTION ID:56
QUESTION ID:57
QUESTION ID:58
QUESTION ID:59
| Column-I | Column-II |
| P. Trisomic | 1. 23 |
| Q. Triploid | 2. 45 |
| R. Monosomic | 3. 47 |
| S. Monoploid | 4. 69 |
QUESTION ID:60
| Reporter gene | Source of gene | Detection/assay |
| P. β-glucuronidase | 1. Aequorea victoria | i. Radioactive assay |
| Q. Green fluorescence protein | 2. Photinus pyralis | ii. Fluorimetric |
| R. Luciferase | 3. E. coli | iii. Fluorescence |
| S. Chloramphenicol acetyl transferase | iv. Luminesc |
QUESTION ID:61
QUESTION ID:62
QUESTION ID:63
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Umbel | i. Pedicularis sp. |
| 2. Raceme | ii. Smilacina sp. |
| 3. Compound determinate | iii. Epilobium sp. |
| 4. Spike | iv. Pelargonium sp. |
QUESTION ID:64
QUESTION ID:65
| Column I | Column II |
P. The process of occupation of a particular area by different plant communities from their birth to maturity | 1. Formation |
| Q. A major ecological unit of vegetation | 2. Consociation |
| R. A smaller unit of plant association | 3. Faciation |
S. A subdivision of plant association which is related to minor differences in temperature and moisture relations | 4. Plant succession |
QUESTION ID:66
QUESTION ID:67
QUESTION ID:68
QUESTION ID:69
QUESTION ID:70
QUESTION ID:71
QUESTION ID:72
QUESTION ID:73
QUESTION ID:74
QUESTION ID:75
QUESTION ID:76
| Group I | Group II |
| (P) Vancomycin | (i) Folate metabolism |
| (Q) Rifampin | (ii) DNA synthesis |
| (R) Puromycin | (iii) Protein synthesis |
| (S) Ciprofloxacin | (iv) RNA synthesis |
| (v) Cell wall synthesis |
QUESTION ID:77
QUESTION ID:78
QUESTION ID:79
| Group I | Group II |
| (P) Blood agar media | (i) Coliforms |
| (Q) Minimal media | (ii) Protease producers |
| (R) Skimmed milk agar media | (iii) Hemolytic microbes |
| (S) Bile salt media | (iv) Lipase producers |
| (v) Autotrophs |
QUESTION ID:80
QUESTION ID:81
QUESTION ID:82
| Group I | Group II | Group III |
| (P) Salmonella typhi | (i) helical | (1) non-motile |
| (Q) Saccharomyces cerevisiae | (ii) rod | (2) amphitrichous |
| (R) Aquaspirillum serpens | (iii) curved rod | (3) peritrichous |
| (S) Vibrio cholerae | (iv) ovoid | (4) polar |
QUESTION ID:83
QUESTION ID:84
| Group I | Group II |
| (P) Ampicillin | (i) 70 % alcohol treatment |
| (Q) 1% glucose in phosphate buffer | (ii) Autoclaving at 15 psi for 15 min |
| (R) Plastic syringe | (iii) Autoclaving at 10 psi for 20 min |
| (S) Luria broth | (iv) Membrane filtration |
| (v) γ-ray irradiation |
QUESTION ID:85
QUESTION ID:86
QUESTION ID:87
QUESTION ID:88
QUESTION ID:89
QUESTION ID:90
QUESTION ID:91
QUESTION ID:92
QUESTION ID:93
QUESTION ID:94
QUESTION ID:95
QUESTION ID:96
QUESTION ID:97
QUESTION ID:98
QUESTION ID:99
QUESTION ID:100
QUESTION ID:101
QUESTION ID:102
QUESTION ID:103
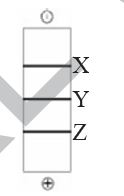
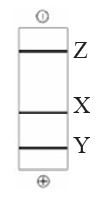
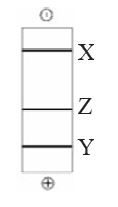
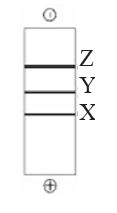
QUESTION ID:104
QUESTION ID:105
QUESTION ID:106
QUESTION ID:107
QUESTION ID:108
QUESTION ID:109
QUESTION ID:110
QUESTION ID:111
QUESTION ID:112
QUESTION ID:113
QUESTION ID:114
QUESTION ID:115
QUESTION ID:116
QUESTION ID:117
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Threonine | 1. Fatty acid |
| Q. Pyridoxine phosphate | 2. Sugar |
| R. Xylose | 3. Amino acid |
| S. Oleic acid | 4. Co-enzyme |
QUESTION ID:118
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Iron | 1. Osteoporosis |
| Q. Calcium | 2. Anemia |
| R. Zinc | 3. Goiter |
| S. Iodine | 4. Dwarfism |
QUESTION ID:119
QUESTION ID:120
QUESTION ID:121
QUESTION ID:122
QUESTION ID:123
Match the following between Group I and Group II in relation to pretreatments
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Ascorbic acid dip | 1. Sogginess in fruits |
| Q. Heat blanching | 2. Minimizes fruit oxidation |
| R. Deaeration | 3. Melting of fat in meat |
| S. Rendering | 4. Removal of odours |
| 5. Minimizes destruction of vitamin C |
QUESTION ID:124
QUESTION ID:125
 TLS Online
TLS Online