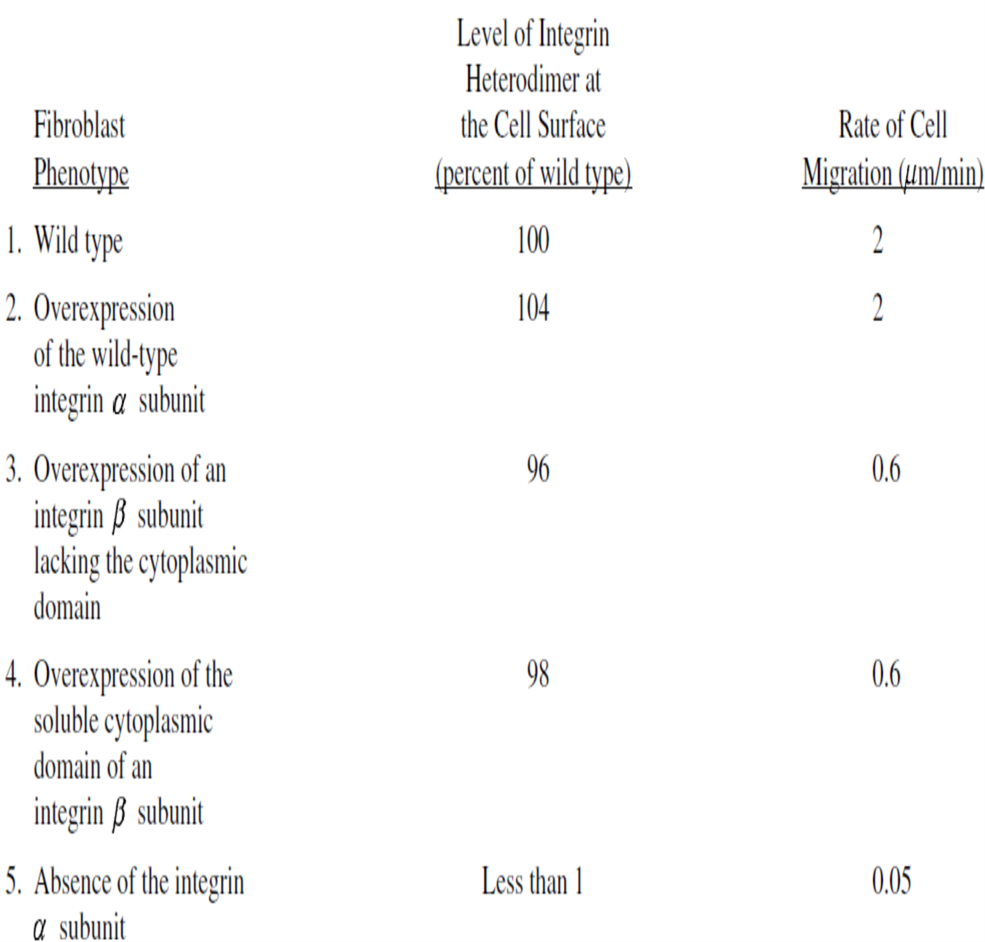
#Question id: 3770
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
Semiconservative replication involves a template. What is the template?
#Question id: 3771
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
In DNA replication, the resulting daughter molecules contain one strand of the original parental DNA and one new strand. What is the explanation for this phenomenon
#Question id: 3772
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
Who performed classic experiments that supported the semiconservative model of DNA replication?
#Question id: 3773
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
DNA contains the template needed to copy itself, but it has no catalytic activity in cells. What catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides in the DNA polymer being formed during DNA replication?
#Question id: 3774
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
Use the figure to answer the following question. Referring to the figure, what bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds?
#Question id: 3775
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
What are telomeres?