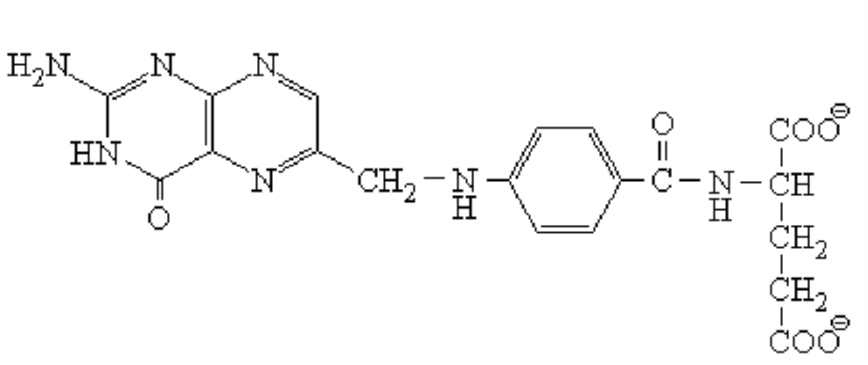
#Question id: 2320
#Unit 2. Cellular Organization
What organelle temporarily stores or transports substances within the cell?
#Question id: 2321
#Unit 2. Cellular Organization
The endosymbiont theory proposes that chloroplasts and mitochondria evolved from ________ and were engulfed by larger ________.
#Question id: 2322
#Unit 2. Cellular Organization
The gelatinous fluid inside the nucleus is called
#Question id: 2323
#Unit 2. Cellular Organization
Prior to replication the DNA in the nucleus is in the form of a tangled mass called
#Question id: 2324
#Unit 2. Cellular Organization
Bacterial DNA is located in:
#Question id: 2325
#Unit 2. Cellular Organization
Which of the following is found in BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?