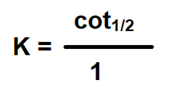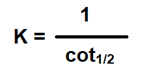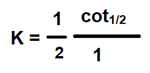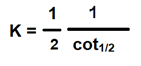#Question id: 3694
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
In eukaryotes, DNA polymerase alpha is a multi-subunit enzyme with different functions. They include:
#Question id: 3695
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
DNA polymerase is highly processive and required for the elongation phase of DNA replication?
#Question id: 3696
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
In eukaryotes, which of the following DNA polymerase is required for mitochondrial DNA replication?
#Question id: 3697
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
In the Meselson-Stahl DNA replication experiment, what percent of the DNA was composed of one light strand and one heavy strand after one generation of growth in 14N containing growth media?
#Question id: 3698
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
In this diagram of the process of DNA replication at a replication fork, the strand labeled B is the:
#Question id: 3699
#Unit 3. Fundamental Processes
In this diagram of the process of DNA replication at a replication fork, the black boxes labeled D and E are: