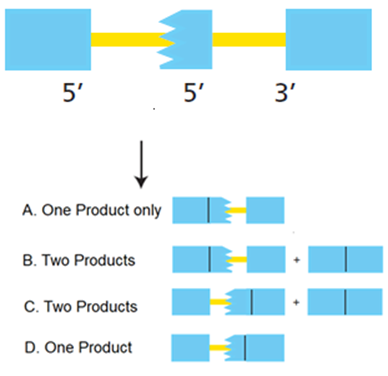
#Question id: 5207
#Unit 11. Evolution and Behavior
Why is it unwise to try to relate an organismʹs complexity with its size or number of cells?
#Question id: 5208
#Unit 11. Evolution and Behavior
Fragments of DNA have been extracted from the remnants of extinct wooly mammoths, amplified, and sequenced. These can now be used to
#Question id: 5209
#Unit 11. Evolution and Behavior
If humans have 2,900 Mb, a specific member of the lily family has 120,000 Mb, and a yeast has ~13 Mb, why canʹt this data allow us to order their evolutionary significance
#Question id: 5210
#Unit 11. Evolution and Behavior
Which of the following is a representation of gene density?
#Question id: 5211
#Unit 11. Evolution and Behavior
Why might the cricket genome have 11 times as many base pairs than that of Drosophila melanogaster?
#Question id: 5213
#Unit 11. Evolution and Behavior
Which of the following is a major distinction between a transposon and a retrotransposon?