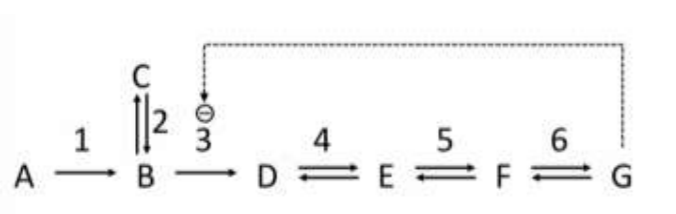
#Question id: 3639
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
Replication of a bacterial chromosome normally starts at a fixed point called:
#Question id: 3640
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
Which of the following is true for the mechanism of excision repair?
#Question id: 3641
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
The point at which separation of the strands and synthesis of new DNA takes place is known as the:
#Question id: 3642
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
Any piece of DNA which replicates as a single unit is called
#Question id: 3643
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
One DNA strand, the______________, is made continuously in a 5→3 direction from the origin.
#Question id: 3644
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
In replication: soon after synthesis, the DNA fragments are joined to make one continuous piece of DNA by the enzyme: