TLS Online TPP Program
More Questions
TLS Online TPP Program
#Question id: 32290
#Unit 1. Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology
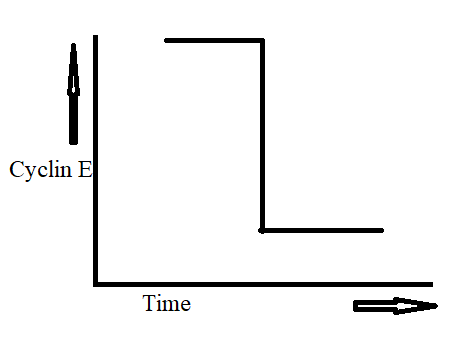
Identify the structure shown
TLS Online TPP Program
#Question id: 32291
#Unit 1. Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology
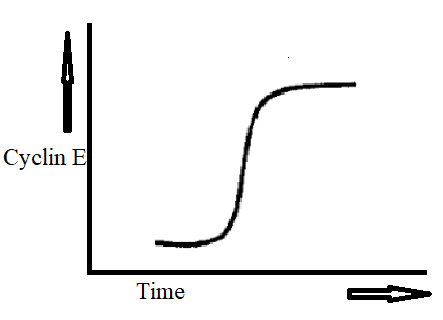
Identify the structure shown
TLS Online TPP Program
#Question id: 32292
#Unit 1. Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology
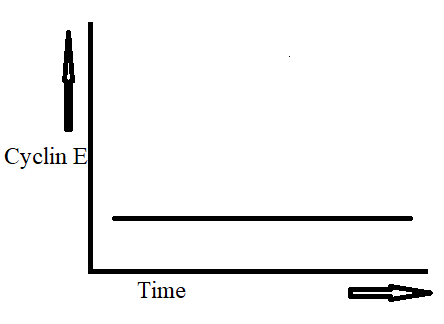
Identify the structure shown
TLS Online TPP Program
#Question id: 32293
#Unit 1. Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology
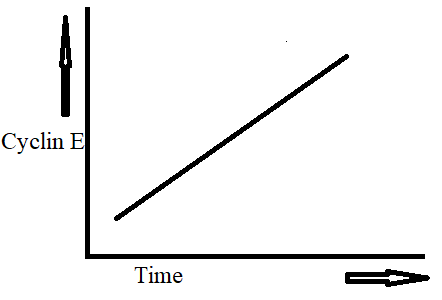
Identify the structure shown
TLS Online TPP Program
#Question id: 32294
#Unit 1. Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology
Identify the structure shown
TLS Online TPP Program
#Question id: 32295
#Unit 1. Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology
Identify the structure shown