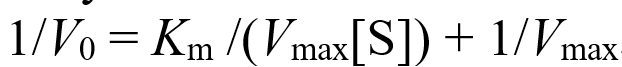#Question id: 10772
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
#Question id: 10773
#Section 3: Genetics, Cellular and Molecular Biology
#Question id: 10774
#Section 6: Plant, Animal and Microbial Biotechnology
Following are a few statements regarding the structure of terpenes:
a) Isopentenyl diphosphate and Dimethyallyl diphosphate are combinely called monoterpene, respectively
b) Isopentenyl diphosphate and Farnesyl diphosphate are Sesquiterpenes and Tetraterpenes
c) Monoterpenes, Sesquiterpenes and Diterpenes have 10, 20 and 30 carbons, respectively
d) Grenyl grenyl diphosphate usually have 20 carbons compound by multiplying with 2X is known as testraterpenes
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
#Question id: 10775
#Section 6: Plant, Animal and Microbial Biotechnology
Geranyl diphosphate is a precursor of which plant hormone biosynthesis?
#Question id: 10776
#Section 6: Plant, Animal and Microbial Biotechnology
pyrethroids that occur in the leaves and flowers of Chrysanthemum species show very striking insecticidal activity. Pyrethroids are________
#Question id: 10777
#Section 6: Plant, Animal and Microbial Biotechnology
Why pyrethroids are synthetically and commercially viable and applicable ?